Rooftop Greenery
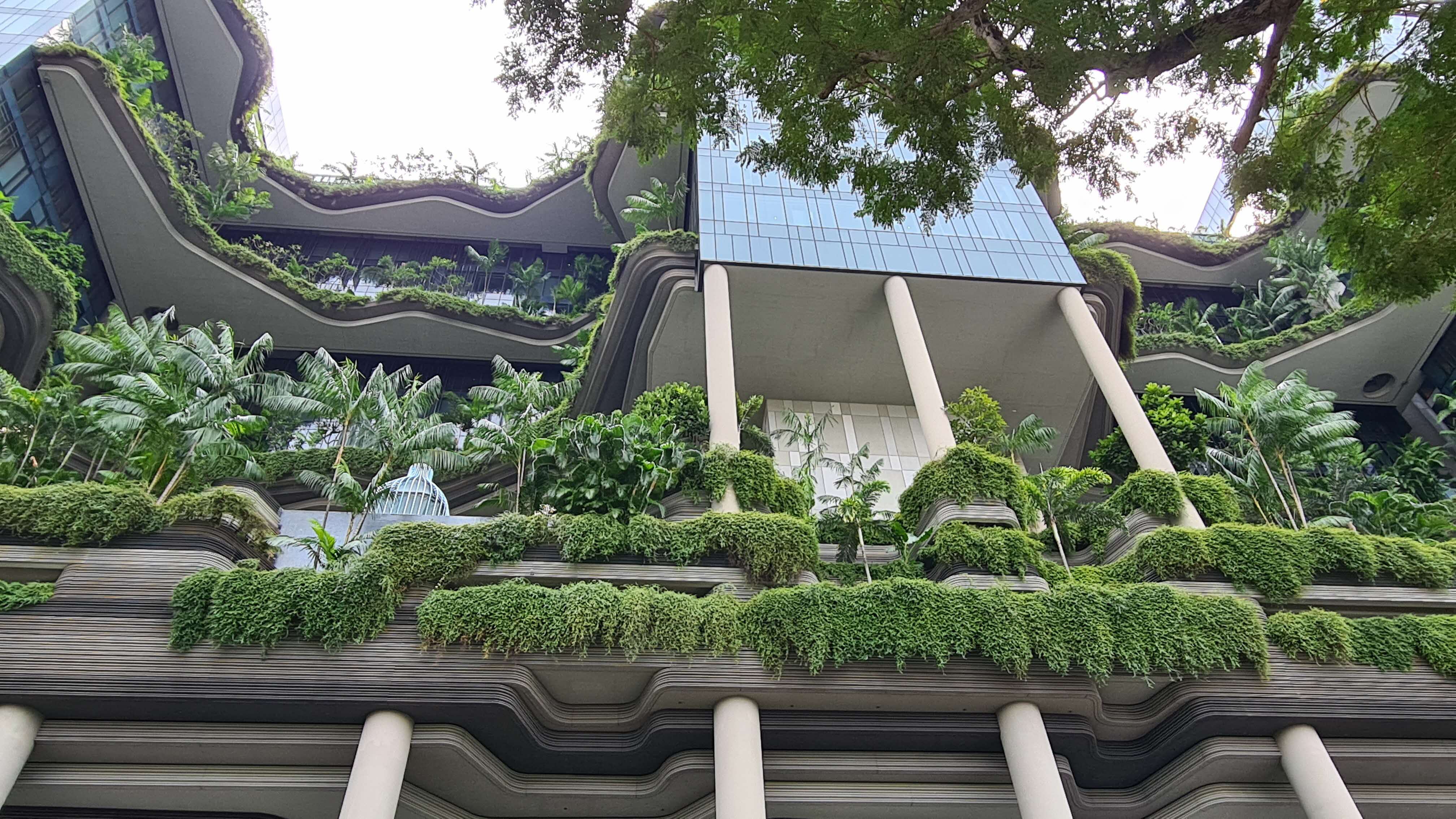

Rooftop greenery refers to the greening efforts and landscaping on the rooftop. When appropriately designed, rooftop greenery can significantly improve building performance, and the benefits includes:
- Reduced urban heat island effect
- Increased energy efficiency
- Enhanced durability of water-proof barriers
- Improved air quality
- Improved acoustic insulation
- Reduced stormwater run off
In general, there are two types of rooftop greenery:
- Green roofs (extensive)
- Roof gardens (intensive)
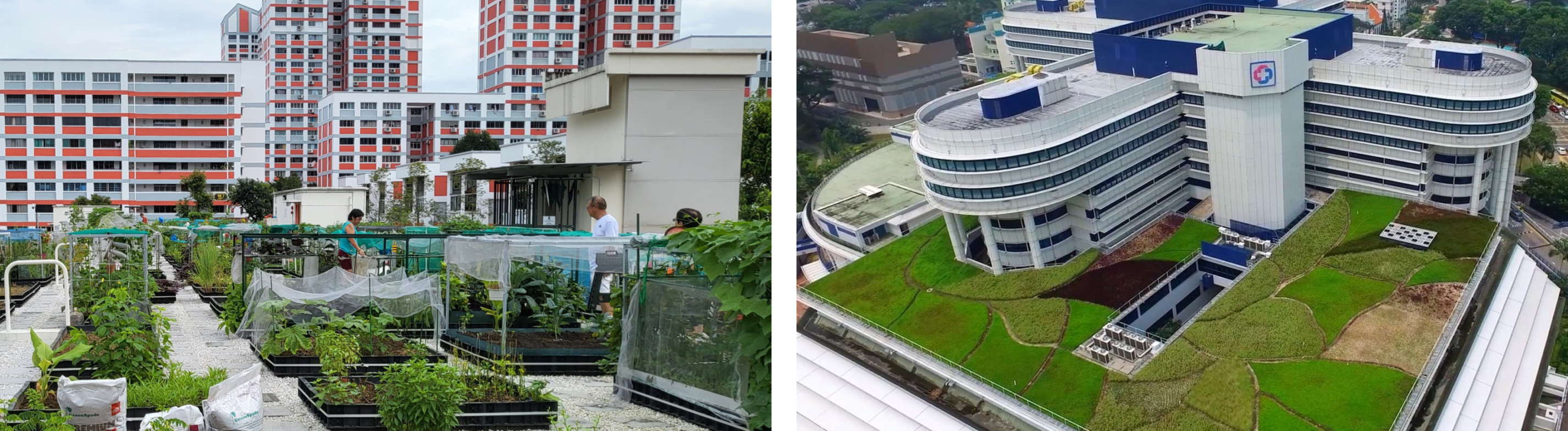 Photographs showing an intensive roof garden (left) on a multi-storey carpark and an extensive green roof (right) on a public healthcare institution
Photographs showing an intensive roof garden (left) on a multi-storey carpark and an extensive green roof (right) on a public healthcare institution
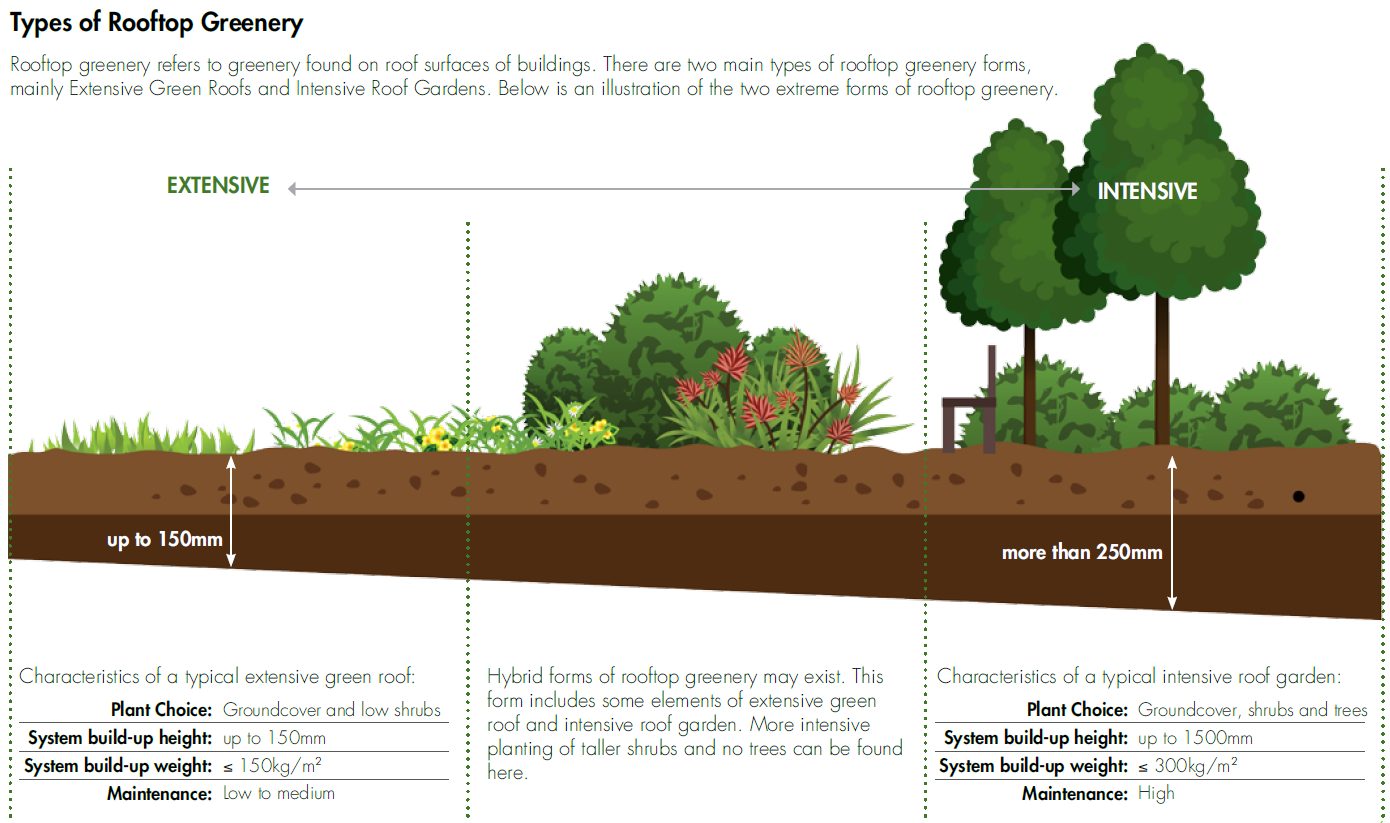
Green Roof (extensive rooftop greenery)
Green roofs are considered extensive in nature and are generally not designed for active recreational use. They are developed mainly for aesthetic and ecological benefits. Generally, these type of roofs are low in installation costs, lightweight (90 - 150 kg/m2) and require minimal maintenance.
Roof Garden (intensive rooftop greenery)
Roof Gardens, on the other hand, are considered intensive in nature and are designed to be accessible. They are often used for recreation and social gatherings, offer spaces for respite and contribute to mental wellbeing.
Components of the Green Roof System
There are five basic components to a green roof system:
- Vegetation/Plant layer
- Substrates and media layer
- Filter layer
- Drainage and storage cells layer
- Protection membrane and root barrier layer
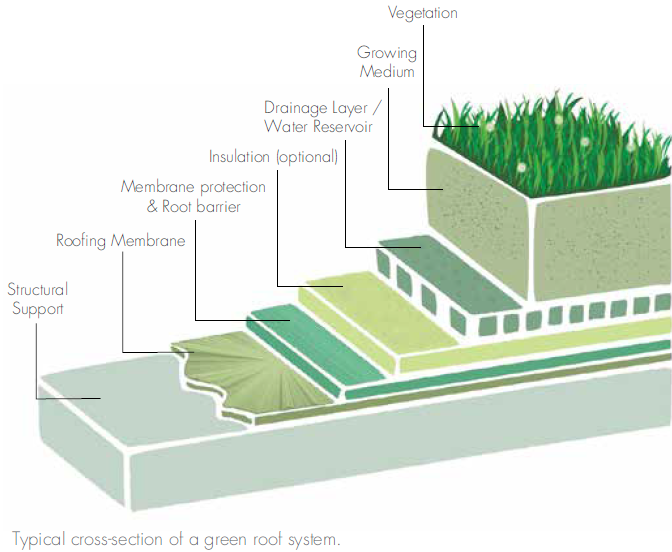
Extensive and intensive green roof systems differ primarily in the thickness and type of growing medium, as well as the species of plants used
Though there are different systems and technology used in the industry, all of them are based on the same component principles. These systems are designed differently in order to meet various site conditions and needs.
The green roof system of an intensive rooftop garden needs a more substantial depth of the substrate/ soil media layer to accommodate the healthy growth of a wider variety of plant species, as compared to a simple extensive green roof.
Rooftop greenery system may be implemented as a modular system or a blanket system. While modular systems are mainly used for extensive green roofs, blanket systems can be used for both intensive and extensive forms.

Plant Selection
Plants chosen for rooftop greenery should typically be able to thrive in drier rooftop conditions, withstand intense sunlight, and tolerate low soil moisture.
- The selection of plants will depend on the following:
- Design objectives (biodiversity attracting, therapeutic benefits, support native plants, improve aesthetics etc.)
- Budget
- Environmental factors
- Depth of the substrate
- Expected level of maintenance
Roof gardens are able to accommodate a wide selection of plants, ranging from ground covers to small trees. The placement of bulkier landscape components such as small trees should consider the efficient transfer of the load throughout the building structures and other safety issues.
Comparatively, green roofs are more suitable for plants that are able to grow in shallow substrates such as groundcover and smaller shrubs.
Head to our plant resources page for recommendations of plants for rooftop greenery.